All The Things You Might Want To Know About Heel Discomfort
Overview
Every mile you walk puts tons of stress on each foot. Your feet can handle a heavy load, but too much stress pushes them over their limits. When you pound your feet on hard surfaces playing sports or wear shoes that irritate sensitive tissues, you may develop heel pain, the most common problem affecting the foot and ankle. A sore heel will usually get better on its own without surgery if you give it enough rest. However, many people ignore the early signs of heel pain and keep on doing the activities that caused it. When you continue to walk on a sore heel, it will only get worse and could become a chronic condition leading to more problems.
Causes
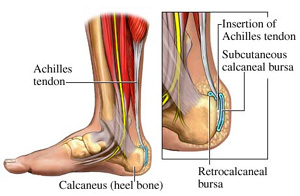
A sharp stabbing pain, like a nail going into the bottom of the heel when first stepping on the foot after getting out of bed or after sitting for period of time, is the most common description for plantar fasciitis or heel spur syndrome. Typically the pain eases off as the day goes on but it may not go away completely. A thick ligament that attaches to the bottom of the heel and runs the length of the foot to the toes can become inflamed and swollen at the attachment site. This tends to be an overuse type of injury where poor foot structure is involved; also, wearing of shoe gear that lacks adequate support (ie: worn out shoes, boots and flip-flops) and prolonged standing or walking are often implicated. A throbbing pain that gets worse as the day goes on and can be worse at night when laying in bed is most often associated with an irritated or entrapped nerve on the inside of the ankle or heel. This is similar to carpel tunnel syndrome in the wrist and hand. Approximately 7 / 10 patients with heel pain have a component of nerve entrapment as the cause of their heel pain. This is also one of the most common causes of chronic heel pain because it is often missed as a diagnosis. When nerve entrapment is considered to be a cause, painless neurosensory testing is performed with the Pressure Specified Sensory Device? (PSSD) at The Foot & Ankle Center, PC to determine the extent of compression. A less common cause of heel pain but a stress fracture is often considered in athletes, such as long distance runners, who have heel pain. Posterior Heel Pain (Retrocalcaneal) This is pain in the back of the heel that flares up when first starting an activity. It is often associated with a large bump that can be irritated by shoes. The Achilles tendon attaches to the back of the heel and, like on the bottom, this attachment site can often become inflamed; a spur may or may not be present. Another painful area is a sac of fluid (bursa) that sits between the tendon and bone to act as a cushion for the tendon. This bursa can become inflamed often leading to significant pain called retrocalcaneal bursitis.
Symptoms
Both heel pain and heel spurs are frequently associated with an inflammation of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot. The inflammation of this arch area is called plantar fasciitis. The inflammation maybe aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support and by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an athletic lifestyle. Achilles Tendinopathy, Pain and inflammation of the tendon at the back of the heel that connects the calf muscle to the foot. Sever?s, Often found in children between the ages of 8 - 13 years and is an inflammation of the calcaneal epiphyseal plate (growth plate) in the back of the heel. Bursitis, An inflamed bursa is a small irritated sack of fluid at the back of the heel. Other types of heel pain include soft tissue growths, Haglunds deformity (bone enlargement at the back of the heel), bruises or stress fractures and possible nerve entrapment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
The following steps may help relieve your heel pain. Use crutches to take weight off your feet. Rest as much as possible for at least a week. Apply ice to the painful area. Do this at least twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, more often in the first couple of days. Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Wear proper-fitting shoes. Use a heel cup, felt pads in the heel area, or shoe insert. Wear night splints. Your doctor may recommend other treatments, depending on the cause of your heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
If treatment hasn't worked and you still have painful symptoms after a year, your GP may refer you to either an orthopaedic surgeon, a surgeon who specialises in surgery that involves bones, muscles and joints or a podiatric surgeon, a podiatrist who specialises in foot surgery. Surgery is sometimes recommended for professional athletes and other sportspeople whose heel pain is adversely affecting their career. Plantar release surgery is the most widely used type of surgery for heel pain. The surgeon will cut the fascia to release it from your heel bone and reduce the tension in your plantar fascia. This should reduce any inflammation and relieve your painful symptoms. Surgery can be performed either as open surgery, where the section of the plantar fascia is released by making a cut into your heel or endoscopic or minimal incision surgery - where a smaller incision is made and special instruments are inserted through the incision to gain access to the plantar fascia. Endoscopic or minimal incision surgery has a quicker recovery time, so you will be able to walk normally much sooner (almost immediately), compared with two to three weeks for open surgery. A disadvantage of endoscopic surgery is that it requires both a specially trained surgical team and specialised equipment, so you may have to wait longer for treatment than if you were to choose open surgery. Endoscopic surgery also carries a higher risk of damaging nearby nerves, which could result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling or some loss of movement in your foot. As with all surgery, plantar release carries the risk of causing complications such as infection, nerve damage and a worsening of your symptoms after surgery (although this is rare). You should discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques with your surgical team.
heel bursitis
Prevention
Wearing real good, supportive shoes are a great way to avoid heel pain. Usually, New Balance is a good shoe to wear, just for everyday shoe gear. By wearing proper footwear and performing thorough stretches, athletes can help prevent frequent heel pain. If you are starting to get a little discomfort or pain in the feet or heel, know that pain is not normal. So if you are having pain, you should be proactive and visit our office. If you let heel pain get out of control you could run into several other problems. It is always suggested to visit a podiatrist whenever you are experiencing pain.

Every mile you walk puts tons of stress on each foot. Your feet can handle a heavy load, but too much stress pushes them over their limits. When you pound your feet on hard surfaces playing sports or wear shoes that irritate sensitive tissues, you may develop heel pain, the most common problem affecting the foot and ankle. A sore heel will usually get better on its own without surgery if you give it enough rest. However, many people ignore the early signs of heel pain and keep on doing the activities that caused it. When you continue to walk on a sore heel, it will only get worse and could become a chronic condition leading to more problems.
Causes
A sharp stabbing pain, like a nail going into the bottom of the heel when first stepping on the foot after getting out of bed or after sitting for period of time, is the most common description for plantar fasciitis or heel spur syndrome. Typically the pain eases off as the day goes on but it may not go away completely. A thick ligament that attaches to the bottom of the heel and runs the length of the foot to the toes can become inflamed and swollen at the attachment site. This tends to be an overuse type of injury where poor foot structure is involved; also, wearing of shoe gear that lacks adequate support (ie: worn out shoes, boots and flip-flops) and prolonged standing or walking are often implicated. A throbbing pain that gets worse as the day goes on and can be worse at night when laying in bed is most often associated with an irritated or entrapped nerve on the inside of the ankle or heel. This is similar to carpel tunnel syndrome in the wrist and hand. Approximately 7 / 10 patients with heel pain have a component of nerve entrapment as the cause of their heel pain. This is also one of the most common causes of chronic heel pain because it is often missed as a diagnosis. When nerve entrapment is considered to be a cause, painless neurosensory testing is performed with the Pressure Specified Sensory Device? (PSSD) at The Foot & Ankle Center, PC to determine the extent of compression. A less common cause of heel pain but a stress fracture is often considered in athletes, such as long distance runners, who have heel pain. Posterior Heel Pain (Retrocalcaneal) This is pain in the back of the heel that flares up when first starting an activity. It is often associated with a large bump that can be irritated by shoes. The Achilles tendon attaches to the back of the heel and, like on the bottom, this attachment site can often become inflamed; a spur may or may not be present. Another painful area is a sac of fluid (bursa) that sits between the tendon and bone to act as a cushion for the tendon. This bursa can become inflamed often leading to significant pain called retrocalcaneal bursitis.
Symptoms
Both heel pain and heel spurs are frequently associated with an inflammation of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot. The inflammation of this arch area is called plantar fasciitis. The inflammation maybe aggravated by shoes that lack appropriate support and by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an athletic lifestyle. Achilles Tendinopathy, Pain and inflammation of the tendon at the back of the heel that connects the calf muscle to the foot. Sever?s, Often found in children between the ages of 8 - 13 years and is an inflammation of the calcaneal epiphyseal plate (growth plate) in the back of the heel. Bursitis, An inflamed bursa is a small irritated sack of fluid at the back of the heel. Other types of heel pain include soft tissue growths, Haglunds deformity (bone enlargement at the back of the heel), bruises or stress fractures and possible nerve entrapment.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
The following steps may help relieve your heel pain. Use crutches to take weight off your feet. Rest as much as possible for at least a week. Apply ice to the painful area. Do this at least twice a day for 10 to 15 minutes, more often in the first couple of days. Take acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain. Wear proper-fitting shoes. Use a heel cup, felt pads in the heel area, or shoe insert. Wear night splints. Your doctor may recommend other treatments, depending on the cause of your heel pain.
Surgical Treatment
If treatment hasn't worked and you still have painful symptoms after a year, your GP may refer you to either an orthopaedic surgeon, a surgeon who specialises in surgery that involves bones, muscles and joints or a podiatric surgeon, a podiatrist who specialises in foot surgery. Surgery is sometimes recommended for professional athletes and other sportspeople whose heel pain is adversely affecting their career. Plantar release surgery is the most widely used type of surgery for heel pain. The surgeon will cut the fascia to release it from your heel bone and reduce the tension in your plantar fascia. This should reduce any inflammation and relieve your painful symptoms. Surgery can be performed either as open surgery, where the section of the plantar fascia is released by making a cut into your heel or endoscopic or minimal incision surgery - where a smaller incision is made and special instruments are inserted through the incision to gain access to the plantar fascia. Endoscopic or minimal incision surgery has a quicker recovery time, so you will be able to walk normally much sooner (almost immediately), compared with two to three weeks for open surgery. A disadvantage of endoscopic surgery is that it requires both a specially trained surgical team and specialised equipment, so you may have to wait longer for treatment than if you were to choose open surgery. Endoscopic surgery also carries a higher risk of damaging nearby nerves, which could result in symptoms such as numbness, tingling or some loss of movement in your foot. As with all surgery, plantar release carries the risk of causing complications such as infection, nerve damage and a worsening of your symptoms after surgery (although this is rare). You should discuss the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques with your surgical team.
heel bursitis
Prevention

Wearing real good, supportive shoes are a great way to avoid heel pain. Usually, New Balance is a good shoe to wear, just for everyday shoe gear. By wearing proper footwear and performing thorough stretches, athletes can help prevent frequent heel pain. If you are starting to get a little discomfort or pain in the feet or heel, know that pain is not normal. So if you are having pain, you should be proactive and visit our office. If you let heel pain get out of control you could run into several other problems. It is always suggested to visit a podiatrist whenever you are experiencing pain.